Alkaline electrolysis
Alkaline electrolysis

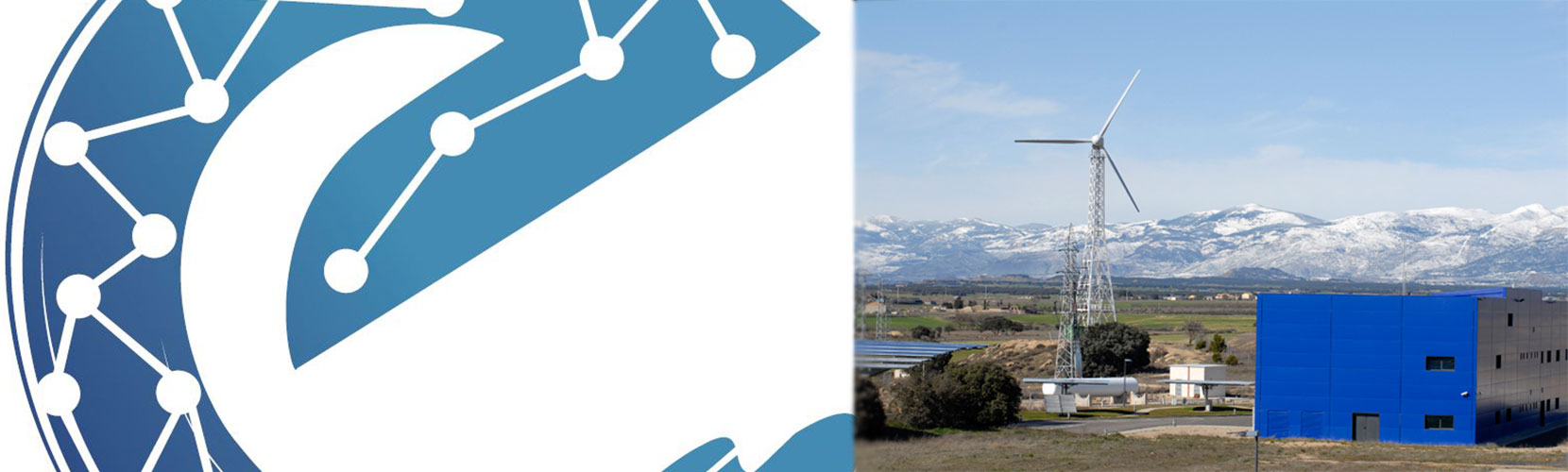
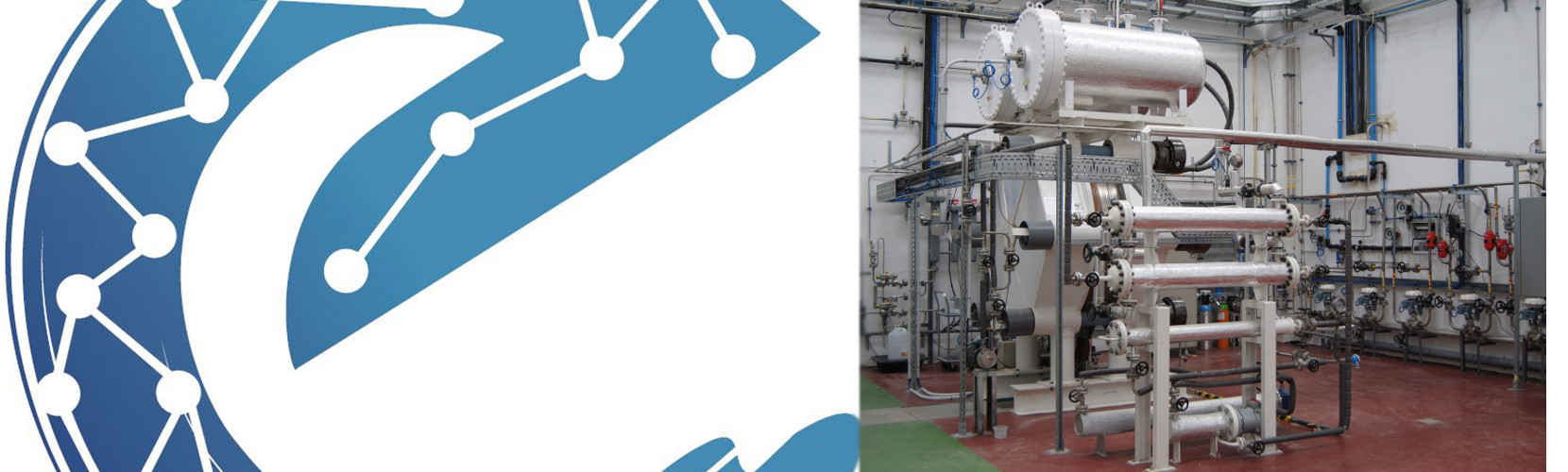
Electrolysers convert water into hydrogen and oxygen gas, throuh the application of a direct current, by an electrochemical process. Alkaline electrolysers, where the electrolyte is a KOH solution, operated at pressure offer an economic and competitive low carbon hydrogen production method.
 Applications
Applications

Electrolysers could provide grid services, helping the energy transition, specially considering an electricity mix with high renewables penetration. Conversion of electricity to hydrogen offers also several applications for the product (hydrogen in mobility, industrial use of the hydrogen).
 Funded by
Funded by

This project has received funding from the Fuel Cells and Hydrogen 2 Joint Undertaking under grant agreement No 671458. This Joint Undertaking receives support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme and Spain, Belgium, Germany, Switzerland.

This work is supported by the Swiss State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation (SERI) under contract number 15.0252.